
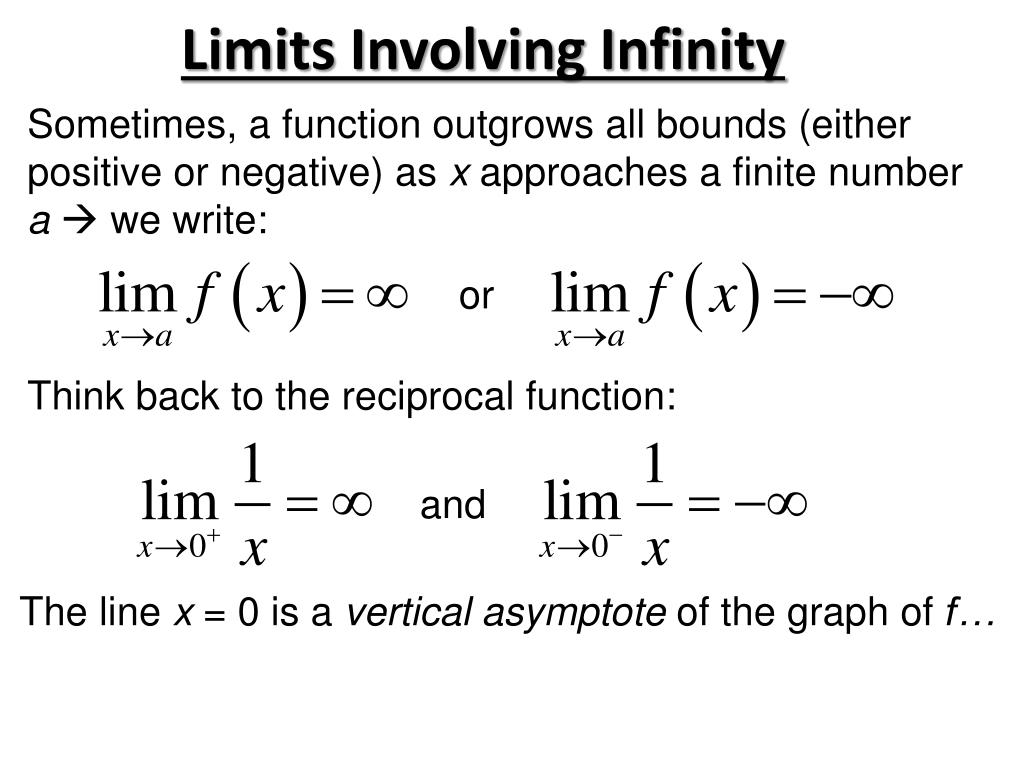
Power law for limits states that the limit of the nth power of a function equals the nth power of the limit of the function.Quotient law for limits states that the limit of a quotient of functions equals the quotient of the limit of each function.Product law for limits states that the limit of a product of functions equals the product of the limit of each function.Constant multiple law for limits states that the limit of a constant multiple of a function equals the product of the constant with the limit of the function.Difference law for limits states that the limit of the difference of two functions equals the difference of the limits of two functions.

Sum law for limits states that the limit of the sum of two functions equals the sum of the limits of two functions.In the image above, the Limit Laws below describe properties of limits which are used to evaluate limits of functions.
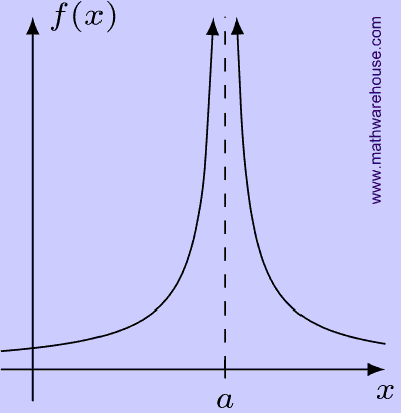
 Indeterminate Forms and L’Hopital’s Rule. Derivatives of Logarithmic and Exponential Functions. Linear Approximations and Differentials. Electronic flashcards for derivatives/integrals. We know that the limit of both -1/x and 1/x as x approaches either positive or negative infinity is zero, therefore the limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches either positive or negative infinity is zero. Since sin(x) is always somewhere in the range of -1 and 1, we can set g(x) equal to -1/x and h(x) equal to 1/x. So, to make calculations, engineers will approximate a function using small differences in the function and then try and calculate the derivative of the function by having smaller and smaller spacing in the function sample intervals. Limits are also used as real-life approximations to calculating derivatives. How Are Calculus Limits Used in Real Life? A few examples are below: In general, you can see that these limits are equal to. The one-sided *right* limit of f at x=0 is 1, and the one-sided *left* limit at x=0 is -1. definition, it is possible to find the value of the limits given a graph. For example, f(x)=|x|/x returns -1 for negative numbers, 1 for positive numbers, and isn't defined for 0. How Do You Know if a Limit Is One-Sided?Ī one-sided limit is a value the function approaches as the x-values approach the limit from *one side only*. Limit, a mathematical concept based on the idea of closeness, is used primarily to assign values to certain functions at points where no values are defined, in such a way as to be consistent with nearby values. When Can a Limit Not Exist?Ī common situation where the limit of a function does not exist is when the one-sided limits exist and are not equal: the function "jumps" at the point. The idea of a limit is the basis of all differentials and integrals in calculus. What Are Limits in Calculus?Ī limit tells us the value that a function approaches as that function's inputs get closer and closer(approaches) to some number. If these values tend to some definite unique number as x tends to a, then that obtained a unique number is called the limit of f(x) at x = a. If at a point x = a, f(x) takes indeterminate form, then we can consider the values of the function which is very near to a. Limits formula:- Let y = f(x) as a function of x. Here are some properties of the limits of the function: If limits \( \lim _\)įAQs on Limits What is the Limit Formula? Let us discuss the definition and representation of limits of the function, with properties and examples in detail. Whereas indefinite integrals are expressed without limits, and it will have an arbitrary constant while integrating the function. For definite integrals, the upper limit and lower limits are defined properly. Generally, the integrals are classified into two types namely, definite and indefinite integrals. The limit of a sequence is further generalized in the concept of the limit of a topological net and related to the limit and direct limit in the theory category. It is used in the analysis process, and it always concerns the behavior of the function at a particular point. Limits play a vital role in calculus and mathematical analysis and are used to define integrals, derivatives, and continuity. Limits in maths are defined as the values that a function approaches the output for the given input values.
Indeterminate Forms and L’Hopital’s Rule. Derivatives of Logarithmic and Exponential Functions. Linear Approximations and Differentials. Electronic flashcards for derivatives/integrals. We know that the limit of both -1/x and 1/x as x approaches either positive or negative infinity is zero, therefore the limit of sin(x)/x as x approaches either positive or negative infinity is zero. Since sin(x) is always somewhere in the range of -1 and 1, we can set g(x) equal to -1/x and h(x) equal to 1/x. So, to make calculations, engineers will approximate a function using small differences in the function and then try and calculate the derivative of the function by having smaller and smaller spacing in the function sample intervals. Limits are also used as real-life approximations to calculating derivatives. How Are Calculus Limits Used in Real Life? A few examples are below: In general, you can see that these limits are equal to. The one-sided *right* limit of f at x=0 is 1, and the one-sided *left* limit at x=0 is -1. definition, it is possible to find the value of the limits given a graph. For example, f(x)=|x|/x returns -1 for negative numbers, 1 for positive numbers, and isn't defined for 0. How Do You Know if a Limit Is One-Sided?Ī one-sided limit is a value the function approaches as the x-values approach the limit from *one side only*. Limit, a mathematical concept based on the idea of closeness, is used primarily to assign values to certain functions at points where no values are defined, in such a way as to be consistent with nearby values. When Can a Limit Not Exist?Ī common situation where the limit of a function does not exist is when the one-sided limits exist and are not equal: the function "jumps" at the point. The idea of a limit is the basis of all differentials and integrals in calculus. What Are Limits in Calculus?Ī limit tells us the value that a function approaches as that function's inputs get closer and closer(approaches) to some number. If these values tend to some definite unique number as x tends to a, then that obtained a unique number is called the limit of f(x) at x = a. If at a point x = a, f(x) takes indeterminate form, then we can consider the values of the function which is very near to a. Limits formula:- Let y = f(x) as a function of x. Here are some properties of the limits of the function: If limits \( \lim _\)įAQs on Limits What is the Limit Formula? Let us discuss the definition and representation of limits of the function, with properties and examples in detail. Whereas indefinite integrals are expressed without limits, and it will have an arbitrary constant while integrating the function. For definite integrals, the upper limit and lower limits are defined properly. Generally, the integrals are classified into two types namely, definite and indefinite integrals. The limit of a sequence is further generalized in the concept of the limit of a topological net and related to the limit and direct limit in the theory category. It is used in the analysis process, and it always concerns the behavior of the function at a particular point. Limits play a vital role in calculus and mathematical analysis and are used to define integrals, derivatives, and continuity. Limits in maths are defined as the values that a function approaches the output for the given input values.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
